Cannabinoids are a group of chemically diverse compounds found in the cannabis plant, which have been used for therapeutic purposes since ancient times. Cannabinoids are believed to have potential medicinal properties but can also have psychoactive effects when consumed.
Cannabinoids interact with cannabinoid receptors located throughout our bodies and brains, leading to various physiological responses. They can affect our moods, pain levels, appetite, memory, sleep patterns, and more.

The two main types of known cannabinoids are phytocannabinoids (occurring naturally in plants) and endocannabinoids (produced by our own bodies).
The most well-known phytocannabinoid is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is another prominent phytocannabinoid and has been found to have many potential therapeutic benefits, such as anti-inflammatory and pain relief properties. Other less-known cannabinoids include cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), and cannabichromene (CBC).
The endocannabinoid system is a biological system within the human body that is composed of two types of receptors interacting with these cannabinoids. The CB1 receptor is mainly found in the brain, whereas the CB2 receptor is located throughout our immune and peripheral nervous systems. When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, they lead to various physiological responses, such as regulating mood, appetite, pain levels, memory, sleep patterns, and more.
History of Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids have been used for therapeutic purposes as far back as ancient times. In the ancient Chinese pharmacopeia, The Divine Farmer’s Herb-Root Classic, it was noted that cannabis could be used to treat various ailments, including pain and inflammation. Evidence of cannabis and cannabinoid use has been around for centuries, as far back as 2000 BC, in regions like India and Central Asia.
But it was not until 1964 that scientists could isolate and identify the first cannabinoid, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), from the cannabis plant. Following this discovery, researchers began exploring how cannabinoids interacted with the body and discovered an endogenous system of receptors known as the endocannabinoid system (ECS). This system comprises two main types of receptors: CB1 and CB2.
The role of these receptors is to regulate various physiological processes, such as mood, appetite, pain levels, memory, sleep patterns, and more. The discovery of the ECS has led to a better understanding of how cannabinoids interact in our bodies and their potential therapeutic benefits for treating ailments like chronic pain or anxiety.
The potential benefits of cannabinoids are only beginning to be explored. Scientists have identified over 100 different types of cannabinoids and are continuing to investigate their medicinal properties.
With more research into the science behind these compounds, we can better understand their therapeutic effects on our bodies and how they can be used beneficially as medicine in the future. As our understanding of cannabinoids deepens, it will open up new possibilities for treating a variety of ailments. We are just at the tip of the iceberg when it comes to researching this fascinating group of chemical compounds.
Popular Cannabinoids and Their Effects on the Body
CBG is known as a “parent” cannabinoid to many other minor cannabinoids. All cannabinoids begin as CBG. To get a little technical, cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is the acidic form of CBG. It’s the chemical precursor for THCA and CBDA, which are the acids that evolve into THC and CBD. These compounds evolve into a usable form when heated by fire (when smoking a bowl or joint, for example) or when turned into vapor.
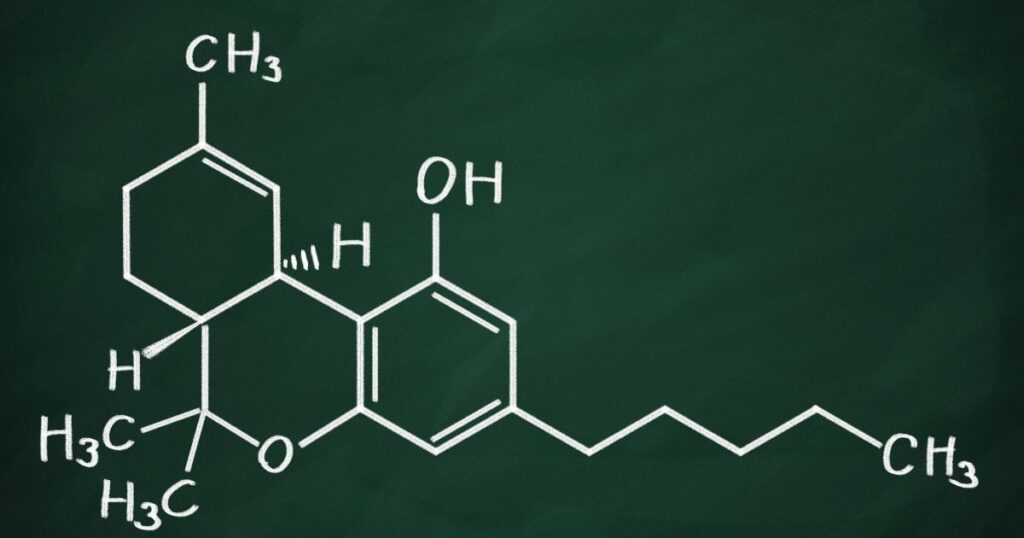
THC is the most well-known cannabinoid and is responsible for producing psychoactive effects when consumed. It can also help reduce inflammation, improve appetite, aid with pain relief, reduce anxiety, stimulate creativity, and increase focus.
CBD is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid that has been found to have potential therapeutic benefits, such as anti-inflammatory and pain relief properties. It can also help modulate the effects of THC in the body, reduce anxiety levels, and provide neuroprotective effects.
CBN is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid found in aged or oxidized cannabis that has been shown to have sedative properties. It can help stimulate appetite, reduce inflammation, and aid sleep cycles.
CBC is another non-intoxicating cannabinoid that has been found to have anti-inflammatory, antidepressant, and analgesic properties. It can also help improve brain function by promoting neural growth and aiding memory formation.
Therapeutic Uses of Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids have shown promise in treating a variety of medical conditions. Here are some of the most notable therapeutic applications:
Pain Management
Cannabinoids, particularly THC and CBD, have been found to be effective in managing chronic pain. They interact with the ECS to modulate pain signals and reduce inflammation, providing relief for conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain.
Epilepsy
CBD has gained significant attention for its anticonvulsant properties. Epidiolex, a CBD-based medication, has been approved by the FDA for treating certain forms of epilepsy, such as Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Clinical trials have demonstrated CBD’s ability to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
Anxiety and Depression
Both THC and CBD have shown potential in treating anxiety and depression. While THC can have anxiety-reducing effects in lower doses, it may exacerbate anxiety in higher doses. CBD, on the other hand, has consistently demonstrated anxiolytic properties without the risk of inducing anxiety, making it a safer option for many individuals.
Neuroprotection
Cannabinoids have neuroprotective properties, which may make them beneficial in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis. They help protect brain cells from damage, reduce inflammation, and promote neurogenesis (the growth of new neurons).
Cancer Treatment
Cannabinoids have been studied for their potential anti-cancer properties. Research suggests that they may inhibit the growth of cancer cells and reduce tumor size in certain types of cancer. Additionally, cannabinoids can help alleviate symptoms associated with cancer and its treatment, such as nausea, vomiting, and pain.
Cannabinoids and Endocannabinoid System
The discovery of cannabinoids has also led to a better understanding of our body’s endocannabinoid system. This system comprises of two main types of receptors: CB1 and CB2, which are found in the brain and throughout our immune and peripheral nervous systems, respectively. When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, they can lead to various physiological responses, including regulating mood, appetite, pain levels, memory, sleep patterns, and more.
The discovery of the ECS has opened up a new world of potential therapeutic applications for cannabinoids. Studies suggest that cannabinoids can be used to treat conditions such as chronic pain, anxiety, depression, and even certain types of cancer.
As we continue to learn more about how these compounds interact with our body’s natural systems, it will provide us with powerful tools to help improve our quality of life and overall health. Thus, showing that this system is essential not only for our health but also for the use and understanding of cannabinoids in medical treatments.
The endocannabinoid system’s discovery has shown us an innate connection between cannabis plants and humans. The fact that our bodies produce their own cannabinoids and recognize similar compounds from cannabis plants suggests we have evolved in a symbiotic relationship with this plant.
This connection may explain why cannabinoids have been used for centuries to help promote balance within our bodies and provide relief from various ailments.
This relationship between humans and cannabis also shows us how powerful nature can be in providing us with healing solutions without relying on synthetic drugs or treatments. As we continue to uncover more about how cannabinoids interact with the body, it will open up new possibilities for using them as medicine to improve quality of life and overall health.
In conclusion, cannabinoids play an important role in the human body and its endocannabinoid system. This relationship between humans and cannabis further shows us just how powerful nature can be when it comes to providing healing solutions.

Research into cannabinoids and their potential therapeutic benefits is only beginning to scratch the surface. Still, it has already shown us that these compounds have a lot of potential for improving our overall health and quality of life.
As we continue to uncover more about how these compounds interact with our bodies, it will open up new possibilities for using them as medicine to promote balance within our bodies.
We are at the forefront of research into cannabinoids, and we can look forward to all the overall benefits that cannabis has to offer.
Keep updated on all the latest news and updates in the Cannabis industry here at Beard Bros Pharms by signing up for our Friday Sesh Newsletter here. Always Dank and Never Spam!
- Delaware’s Recreational Cannabis Market Finally Set to Launch After Years of Challenges
- Excise Tax Increase to 19% and Its Impact on California Retailers
- Nebraska’s Governor Approves Emergency Medical Cannabis Regulations
- We Must Advocate for Fair and Accurate Marijuana Impairment Testing Policies
- The Global Roots of Plant Medicine: Why Cannabis Has Always Been Part of the Plan
- Military Construction and Veterans Affairs Bill Amendments Could Change Medical Marijuana and MDMA-Assisted Therapy Options for Veterans